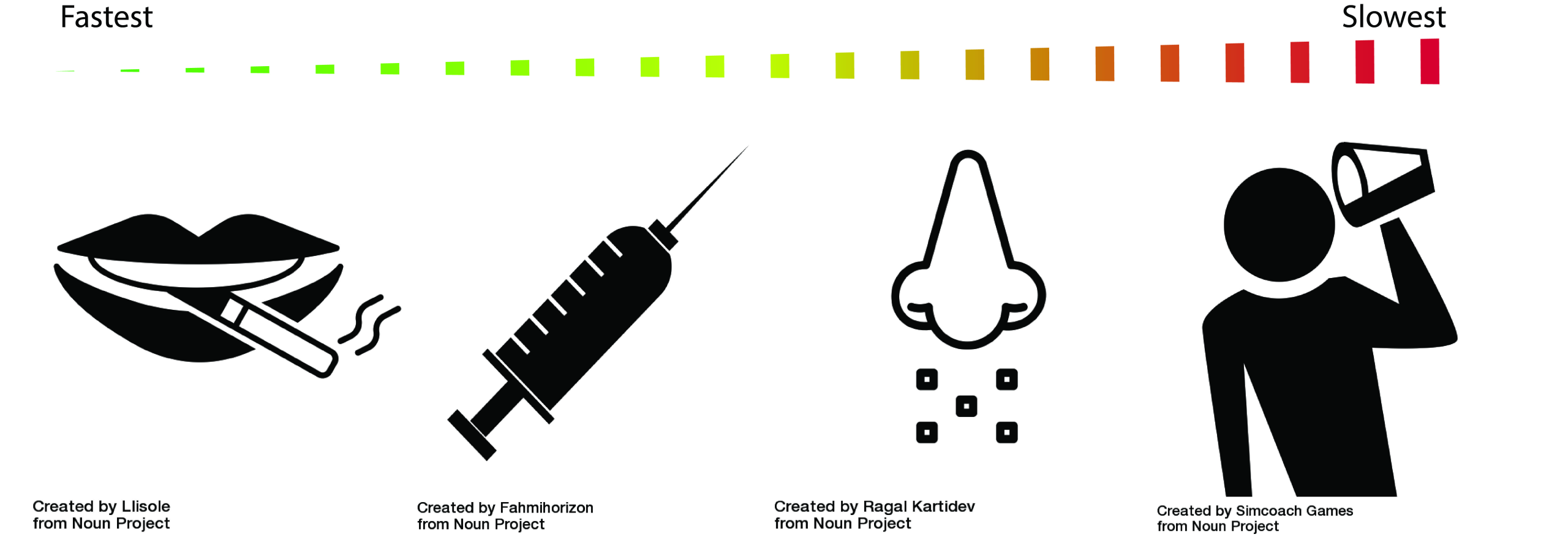
Research has shown that the faster a drug reaches the brain, the more likely it is to be addicting. Different methods of delivery smoking, injecting, or snorting largely influence how quickly a drug reaches the brain. Delivery methods, genetics, and environment all influence the potential of a drug to cause addiction.
The Fastest Way to the Brain
The fastest way to get a drug to the brain is by smoking it. When a drug like tobacco smoke is taken into the lungs, nicotine (the addictive chemical in tobacco) seeps into lung blood where it can quickly travel to the brain. This fast delivery is one reason smoking cigarettes is so addicting. Injecting a drug directly into a blood vessel is the second fastest way to get a drug to the brain, followed by snorting or sniffing it through the nose. A slow mode of delivery is ingestion, such as drinking alcohol. The effects of alcohol take many minutes rather than a few seconds to cause behavioral and biological changes in the brain.
Nobody likes to wait, so users often choose a delivery method that gets them higher faster. As addiction progresses, users seek out the more immediate and more intense high. Speed doesn’t seem to be the only reason that rapid delivery is an important factor in addiction. Recent evidence suggests that the mode of delivery can influence which part of the brain is most affected by a drug. Rapid delivery, such as smoking, affects brain regions that facilitate addiction.
Increased knowledge about drug delivery methods is leading to new addiction therapies. It turns out that delivering a drug slowly, by ingestion or through the skin, produces a weaker, longer-lasting effect. Slow delivery allows the drug to temporarily stabilize the brain and help reduce withdrawal symptoms over a longer period. And slow delivery is less addicting! So it’s becoming an increasingly popular treatment approach.
Reference
| OpenAI. (Year). ChatGPT (Month Day version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com |
| APA reference entry |
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Feb 13 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com |
| APA in-text citation |
(OpenAI, 2023) |