2.0 | Economic Principles in Agriculture
Anthony Farao
🔍 Chapter Overview
This chapter introduces fundamental economic concepts as they apply to decision-making in agricultural business. Students will explore how scarcity influences choices, how opportunity cost drives strategy, and how supply and demand interact in the ag market. The chapter concludes by examining how risk and uncertainty shape agricultural decisions, setting the stage for more advanced management principles in later weeks.
📂 2.1 Scarcity, Opportunity Cost, and Economic Decision-Making
Key Concepts:
-
Definition of scarcity in the context of natural, financial, and labor resources
-
The economic problem: unlimited wants vs. limited resources
-
Opportunity cost: choosing one use of resources over another
-
The role of trade-offs in agricultural decision-making
-
Agricultural examples: choosing between crops, livestock investment, equipment upgrades
Practice Reflection:
Think about a time when you or someone in agriculture had to make a difficult choice. What was the opportunity cost?
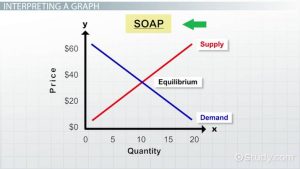
📊 2.2 Supply, Demand, and the Ag Market
Key Concepts:
-
Law of Demand: as price increases, quantity demanded decreases (and vice versa)
-
Law of Supply: as price increases, producers are willing to supply more
-
Equilibrium price: where supply equals demand
-
Shifts in supply and demand (causes and effects): weather events, global markets, consumer trends
-
Real-world agricultural market examples: dairy pricing, almond exports, seasonal produce fluctuations
Practice Questions:
-
What factors might cause the demand for beef to increase?
-
If the supply of water decreases in California, how does that affect the ag market?
🎯 2.3 Risk and Uncertainty in Ag Economics
Key Concepts:
-
The difference between risk (known probabilities) and uncertainty (unknown outcomes)
-
Common risks in agriculture: weather, disease, market volatility, input costs
-
Decision-making under uncertainty: the importance of data, experience, and insurance
-
Tools for risk management: diversification, futures markets, crop insurance
Real-World Insight:
Explore how a local farmer might hedge against future input cost increases by forward contracting or investing in automation.
Reflection Prompt:
In your opinion, which is harder to manage in agriculture—natural risks (like drought) or market risks (like price drops)? Why?
🧠 Chapter Summary
Economic principles provide a framework for making informed decisions in agribusiness. From evaluating opportunity costs to understanding how market prices are set and how to respond to risk, this chapter equips students with the foundational tools for business success in an unpredictable agricultural environment.
Media Attributions
- Supply and Demand Curve
